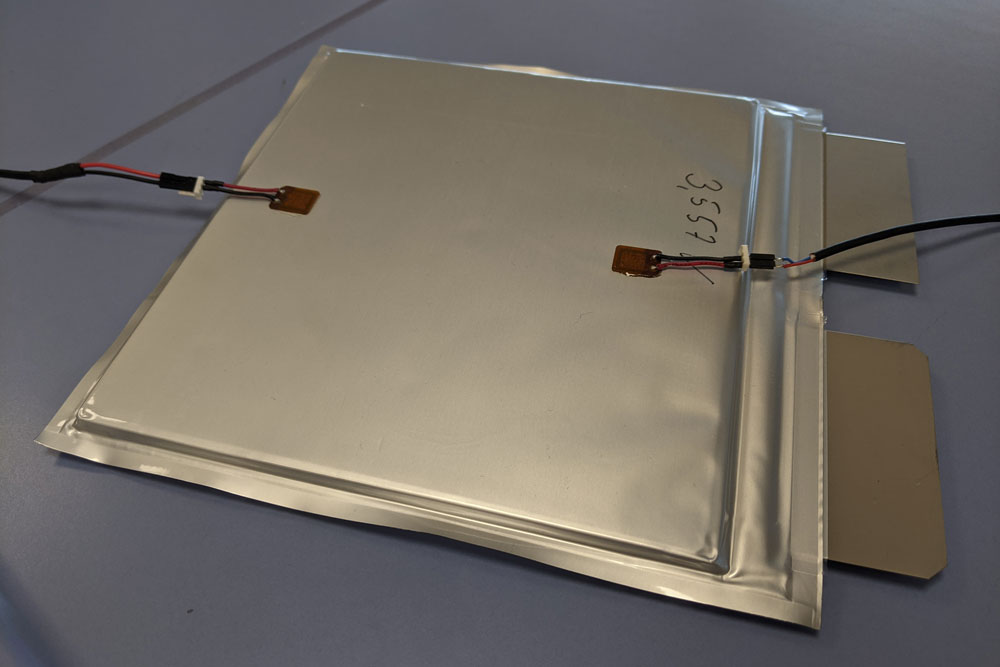
Since their introduction to the market in the 1990s, lithium-ion batteries have been used in many applications, including everyday devices such as smartphones and laptops, as well as more specialized applications such as autonomous underwater vehicles (AOVs). For this application in particular, battery monitoring is extremely important to ensure safe and effective operation.
At Fraunhofer SOT, novel battery condition monitoring methods have been developed in collaboration with Fraunhofer IKTS, targeting underwater applications such as ROVs, AOVs or submarines.
Our techniques are based on the use of piezoelectric transducers and the ultrasonic waves (guided waves) they generate, which propagate inside the battery and interact with its components. This so-called "Guided Waves Battery Monitoring" uses the effect that during charge and discharge cycles and battery degradation, the mechanical properties of the battery components change, thus affecting the propagation of the guided ultrasonic waves. This allows the wave parameters and the mechanical properties of the battery to be correlated and the State of Charge (SoC) and State of Health (SoH) of the battery to be determined.
Our techniques, applicable to any type of battery design and chemistry, offer:
- Accurate SoC and SoH determination
- Increased operational safety
- Longer time under water
- Longer battery life
- Increased stability and reliability
- Battery degradation prediction